You might have come across the phrase “sales vs. presales“ and wondered what the difference is.
While both roles aim to win business and serve the client’s needs, presales professionals ensure that the solution is technically sound and meets the client’s requirements, whereas sales professionals focus on building relationships, negotiating terms, and closing the deal.
Effective collaboration between presales and sales teams is crucial for a successful sales strategy.
It’s no secret that refining the sales sequence is essential to a company’s success. But what is less known is that presales – the process of identifying and qualifying potential customers – are just as crucial, if not more so.
Harvard Business Review reports that companies with successful implementation of presales processes often secure win rates between 40–50% for new business and 80–90% for renewals.
You see, investing in presales will work wonders in your sales pipeline.
Before we move into the significant differences between these terms, let us first define them.
Key Takeaways
- Presales is crucial for laying the groundwork for successful transactions by establishing and nurturing relationships with potential customers, ultimately bridging the gap between customer expectations and company offerings.
- While sales teams focus on meeting revenue targets and closing deals, presales teams support sales by providing technical expertise, product knowledge, and resources to ensure sales representatives are prepared to strategically sell the offer.
- Presales involves tasks completed before a sale, such as lead identification, qualification, nurturing, and proposal crafting. On the other hand, sales processes begin after lead generation, involving engagement, negotiation, order fulfillment, and upselling, supported by tools like proposals, contracts, and demos.
Definitions
Let’s go over the definitions of each term.
What is Presales?
Presales refers to the activities done before a customer makes a purchase.
Before a sale takes place, companies often leverage presales activities to establish and nurture relationships with potential customers.
From creating tailored marketing materials to organizing events connecting buyers and sellers, these efforts can provide the groundwork for successful transactions.
A vital component of presales operations is customer analysis, which helps salespeople understand their target audience better through surveys and data reviews.
The purpose of presales is to bridge the gap between customers’ expectations and company offerings by helping customers arrive at the best possible decision for their specific needs.
What is Sales?
Sales is the process of closing the deal—convincing the customer to make the purchase and completing the transaction. The seller completes a transaction in response to an inquiry, offer, bid, or proposal.
Direct sales activity involves the actual process of selling, which is more relationship-driven and aims to close deals.
A sale is considered to be complete when:
- The buyer and seller agree on the price and quantity of goods or services
- Both parties exchange something of value
- The title to the goods or services passes from the seller to the buyer.
Differences
Presales and sales represent the dynamic between the customer and the company. Without a strong presence in either department, an organization may find it difficult to move products or services from concept to reality.
The sales funnel describes the various stages involved in the sales process, with presales activities playing a crucial role at the beginning of this funnel. These activities are integral to improving future sales through process optimization and collaboration with sales teams.
Sales teams are responsible for meeting and exceeding quotas by selling products or services to customers. Pre-sales teams are accountable for supporting the sales team in achieving their quotas.
Let’s explore their differences in goals, roles, processes, and tools.
Goals
The goal of presales is to enable the sales team.
So, the pre-sales team needs to have a deep understanding of their offer and communicate that understanding to the sales rep. Presales also supports the sales team by providing them with tools, information, and resources.
In short, the presales goal is to ensure that the sales team is as prepared as possible to sell the offer. Additionally, effective presales activities play a crucial role in retaining existing customers and maintaining customer loyalty.
The goal of sales is to sell the product or service.
Revenue growth is the ultimate target, but sales teams also focus on other metrics, such as the number of deals closed or the amount of new business generated.
Roles
The presales team typically consists of account managers, business development representatives (BDRs), and product specialists.
- Account managers oversee the relationships with key accounts.
- BDRs are responsible for generating new leads and opportunities.
- Product specialists provide in-depth product knowledge to the sales team and support them during the sales processes.
The sales team typically consists of sales development representatives (SDRs), account executives, and closing managers.
- SDRs are tasked with generating new leads and opportunities.
- Account executives are responsible for managing relationships with key accounts and closing deals.
- Closing managers are responsible for overseeing the entire sales cycle and ensuring that deals are closed in a timely manner.
Process
The Pre-sales Process
Presales requires tasks necessary to be completed before a product or service is sold.
Presales generally involves five key steps:
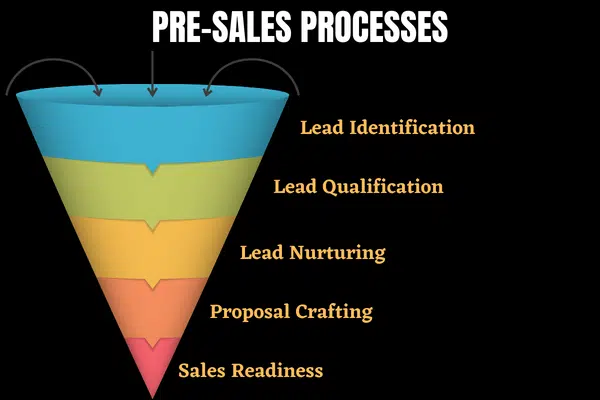
- Lead Identification: Identifying the right prospects for your business so that you can focus on those most likely to become customers.
- Lead Qualification: Evaluating leads against established criteria to determine which leads are more likely to convert.
- Lead Nurturing: Developing relationships with potential customers through education and value-adding content.
- Proposal Crafting: Creating tailored proposals that appeal to each customer’s needs and situation.
- Sales Readiness Preparing your team for sales conversations, including product demos and sales decks.
The Sales Process
The sales process begins after a lead has been generated. Direct sales activity involves the actual process of selling, which includes engagement, negotiation, and closing deals.
The sales process also involves five key steps:
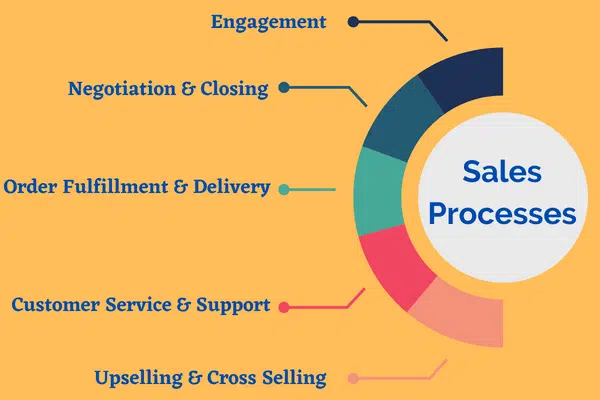
- Engagement: Reaching out to stakeholders and building relationships between them and the company.
- Negotiation & Closing: Exploring different options, discussing terms, and closing deals that make mutual sense for both parties involved.
- Order Fulfillment & Delivery: Ensuring orders have been processed correctly and delivered on time to meet customer expectations.
- Customer Service & Support: Building strong relationships with customers through timely support and delivering a high-quality product or service experience throughout the customer journey as well as after they’re already satisfied customers.
- Upselling & Cross Selling opportunities: Proactively looking at opportunities for pipeline velocity by offering related products or services alongside existing ones being purchased by customers
Tools
Because of the differences mentioned above, the tools can also vary. For example, presales teams may use marketing automation software to nurture leads, while sales teams may use customer relationship management (CRM) software to monitor customer data and manage deals.
We’ll give you a rundown of the most commonly used tools in pre-sales and sales so that you can be better prepared for success.
Pre-Sales Tools
As the primary goal of pre-sales is generating interest, pre-sales teams often use tools like webinars, eBooks, white papers, and free trials.
- Webinars: virtual events that allow you to present information about your product or service to a large group of people at once.
- eBooks: digital books that are packed with information about a particular topic.
- White papers: similar to eBooks, but they tend to be shorter—around 5,000 words—and more focused on providing detailed information about a specific issue or problem.
- Free trials: allow potential customers to use your product or service for a limited time without committing to purchasing it outright. It can effectively generate interest and get people hooked on your product before they’ve even paid for it.
Sales Tools
Once you’ve generated interest in your product or service, it’s time to start selling. The most common sales tools are:
- Proposals: outline what you’re offering and how much it will cost
- Contracts: spell out the terms of the agreement between you and the customer
- Pricing tables: provide a breakdown of the costs associated with your product or service
- Demos: allow potential customers to see your product or service in action to understand better how it works and what it can do for them.
Roles and Responsibilities
- Presales:
- Responsibilities: Create a detailed list of the tasks typically handled by presales, including qualifying leads, conducting technical discovery, hosting demos, responding to RFPs, preparing presentations, and providing technical support during the sales process(
- Skills Required: Emphasize the technical expertise, customer analysis, competitive research, and problem-solving skills needed(
- Tools and Techniques: Mention specific tools presales teams might use (e.g., CRM systems, proposal management software, demo tools). Discuss how automation is streamlining presales efforts.
- Inter-team Collaboration: Explain how presales collaborates with marketing and product teams to ensure alignment before a sales engagement(
- Sales:
- Responsibilities: List typical tasks, such as prospecting, building relationships, negotiating, and closing deals. Mention ongoing customer support for retention(
- Skills Required: Highlight the importance of communication, negotiation, empathy, and persuasion in sales(
- Tools and Techniques: Explain how salespeople use CRM, sales engagement platforms, and other software for managing their pipeline and tracking interactions with prospects.
Best Practices for Creating a Presales Process
Creating an effective presales process requires careful planning, execution, and continuous improvement. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Define Clear Goals and Objectives: Establish clear goals and objectives for the presales process, ensuring they align with the overall sales strategy. This provides a roadmap for the presales team and helps measure success.
- Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish KPIs to measure the effectiveness of the presales process. Metrics such as lead qualification rates, conversion rates, and sales cycle length can provide valuable insights into performance and areas for improvement.
- Develop a Structured Process: Create a structured presales process that includes clear stages, tasks, and timelines. This ensures consistency and helps the presales team stay organized and focused.
- Train and Enable Sales Teams: Provide ongoing training and enablement to sales teams to ensure they have the necessary skills and knowledge to execute the presales process effectively. This includes product training, sales techniques, and understanding customer needs.
- Continuously Monitor and Improve: Continuously monitor the presales process and make improvements as needed. Regularly review performance data, gather feedback from the sales team, and adjust strategies to optimize results.
By following these best practices, businesses can create a robust presales process that supports their sales teams and drives better sales outcomes.
Increasing the Chances of Closing Deals in the Sales Funnel
When you’re selling to another business, you’re not just trying to sell them on your product or service—you’re also trying to sell them on the idea that doing business with you will be a good investment.
A. How to Increase the Chances of Closing a Presale?
Here are proven steps you can do to increase the chances of closing a B2B presale.
A.1 Do Your Research
One of the most important things you can do when preparing for a B2B presale is to research your potential customer. It includes everything from their company history and size to their specific needs and pain points. The more you know about your potential customer, the better equipped you’ll be to sell them your product or service.
In addition to researching the company itself, it’s also a good idea to research the decision-makers within the company. It means finding out who their boss is, what their job title is, and what their role is within the company. The more information you have about those who will be deciding to do business with you, the better.
A.2 Court the Decision-Maker
Once you’ve done your research, it’s time to start building a relationship with the decision-maker. It means reaching out and making contact in a way that is professional and respectful. You want to show them that you’re interested in doing business with them and have something valuable to offer.
One of the best ways to court a decision-maker is to connect with them on LinkedIn. This professional networking site allows you to build relationships and exchange messages with potential customers without being too pushy or sales-y.
A.3 Make a Good First Impression
When you finally meet with the decision-maker, making a good first impression is important.
Another important tip for increasing your chances of closing a B2B presale is to build a relationship with your potential customer before you even start talking about your product or service.
Remember, when you’re selling to another business, you’re not just selling them on your product—you’re also selling them on the idea of doing business with you. So, they must see you as someone they can trust and depend on.
One way to build this relationship is by offering helpful resources.
They could be blog posts, articles, white papers, etc. Something that sells value and addresses the needs of your potential customers. Doing this can position yourself as an expert in your industry and someone who is truly invested in helping businesses succeed.
A.4 Have a Solid Proposal
When you’re ready to start talking specifics about your product or service, it’s important that you have a solid proposal prepared.
This proposal should outline all of your offer’s features and benefits and how they address your potential customer’s specific needs. It should also include pricing information and any special offers or discounts that may be available.
Be sure to keep your proposal complete but concise. You want it easy for decision-makers to digest quickly so they can see how working with you will benefit their business bottom line.
Bonus Tip: The presales questioning technique.
Knowing your customer’s decision criteria is essential when presenting a solution. The “pre-sales questioning technique” provides an effective tool for helping you understand where the client stands so that you can identify any gaps in their decision-making journey.
Doing this twice during the presentation (at the end of summarizing and after fulfilling the criteria) allows customers to be more comfortable with what they’re about to decide on.
B. How to Increase the Chances of Closing a Sale?
Let’s look at four tips for helping you close more deals and grow your business.
B.1 Use the Research from Presales
One of the most important data you can use to increase your closing rate is the research you did during the presales process. It means going into sales calls with as much information as possible about your potential customer.
You should also do additional research on your industry and your competition. Knowledge will help you answer questions and address concerns with confidence which potential customers find outstanding.
B.2 Nurture Relationships
People only do business with businesses they like and trust. Therefore, it’s important that you take the time to build relationships with your potential customers, focusing on retaining existing customers as a key aspect of nurturing these relationships.
Get to know them personally, and let them get to know you. The more comfortable they are with you, the more likely they’ll be to do business with you when the time comes. That’s why relationship marketing must go together with customer marketing.
B.3 Be Persistent (But Not Pushy)
When you believe in what you’re selling, you must be persistent in your efforts to close a deal. However, there is a fine line between being persistent and being pushy.
No one likes to be sold to, so you must balance being assertive and respecting your potential customers’ boundaries.
If someone isn’t interested in what you’re selling, don’t waste your time trying to force them into a sale. Move on and focus your efforts elsewhere.
B.4 Offer Something Differentiated
If your product or service is the same as everyone else’s on the market, it will be difficult to close a sale. Therefore, you must take the time to identify what makes your offering unique and emphasize those differences in your sales pitch.
In closing sales, there are always three possible outcomes: a successful “yes,” an unfortunate “no,” or a lesson.
Here’s a video that teaches how to prepare for both “hell yes” and “hell no” responses from prospects and avoid getting stuck in between.
The Importance of Presales in the Sales Lifecycle
Presales plays a critical role in the sales lifecycle, setting the stage for successful sales outcomes. Here are some reasons why presales is important:
- Qualifies Leads: Presales helps to qualify leads, ensuring that sales teams focus on high-quality opportunities that are likely to convert. This saves time and resources by directing efforts towards the most promising prospects.
- Builds Relationships: Presales helps to build relationships with customers, establishing trust and credibility. By engaging with potential customers early in the sales process, presales teams can lay the foundation for long-term partnerships.
- Provides Valuable Insights: Presales provides valuable insights into customer needs and preferences. This information enables sales teams to tailor their sales approach to meet those needs, increasing the likelihood of a successful sale.
- Reduces Sales Cycle Length: Presales can help to reduce the sales cycle length by identifying and addressing potential objections and concerns early in the sales process. This proactive approach can lead to quicker decision-making and faster sales closures.
Presales is an essential component of the sales process, helping to qualify leads, build relationships, provide insights, and reduce the sales cycle length. By investing in a strong presales function, businesses can improve their overall sales performance and achieve better results.
Closing Statement
The collaboration between sales and presales teams is essential during both the implementation and closing phases, as they work together to support successful product implementation, identify areas for improvement, and maintain communication during negotiations to ensure a seamless closing experience.
FAQs
Here are other frequently asked questions about presales vs. sales that we have not covered in the article.
Is presales part of sales?
Yes. Presales is a part of the integrated sales process responsible for setting the stage for a successful sale. By identifying and addressing potential objections upfront, the presales team can help to smooth the way for a closed deal.
When is the best way to transition from presales to sales?
Most companies will want their presales professionals to transition into sales once they understand the product or service, the market, and the customer. Many companies also prefer that presales professionals have some experience in sales so they can hit the ground running when they transition.
What is the difference between pre-sales and post-sales?
Pre-sales is the process of qualifying and targeting potential customers. It’s about identifying who is a good fit for your product and getting them interested in what you have to offer. Post-sales is turning those interested potential customers into actual paying customers and then supporting them so they become happy, loyal customers.
What are sales automation tools?
These tools help automate routine tasks such as data entry, lead qualification, and follow-up emails. By handling these repetitive tasks, sales reps can focus on high-value activities like building relationships and closing deals.